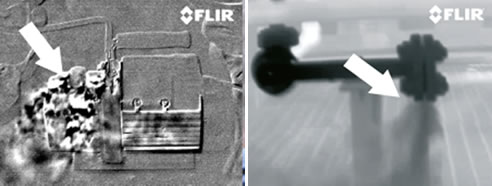
NEWS ARTICLE ARCHIVESOptical Gas Imaging Camera from FLIR Ten tips to get the most out of your Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) camera Optical Gas Imaging (OGI) cameras use spectral wavelength filtering and sterling cooler cold filtering technology to visualize the infrared absorption of VOC/Hydrocarbon, SF6, refrigerants, Carbon Monoxide and other gases whose spectral absorption matches the response of the camera. By using OGI technology, the industry is able to incorporate a 'Smart LDAR' (Leak Detection and Repair) program that allows operators to safely and efficiently visualize gas leaks. OGI has allowed the industry to reduce industrial emissions and operators to conform to future regulations. In addition, OGI saves money, as part of a much more efficient process, but most importantly it improves the safety of their assets and their personnel. To get the most out of your OGI equipment, you should consider the following ten tips. 1. Understand the application and needs. Different applications require different cameras. In other words: one camera may not see all the gases, so you need to understand which type of gas you are dealing with. For example, a VOC/Hydrocarbon OGI camera will not see SF6 and a CO camera will not see refrigerants.
2. Take into account the environmental conditions. The success of passive optical gas imaging depends on environmental conditions. The greater the background energy differential, the easier the camera will be able to visualize the gas leak and pinpoint its source. Active optical gas imaging (i.e. using a laser based backscattering technique) relies on a reflective surface in the background. This presents a significant challenge when you are looking at components high up and pointing the camera at the sky. Also, rain and strong winds need to be taken into account. Rain can make detection very difficult, but wind can actually help visualize the gas because it makes the gas move. 3. Keep in mind that optical gas imaging is qualitative, not quantitative. Due to the environmental variants, background energy differential and variations, an OGI camera will not be able to tell which amount of gas is leaking or what gas it is. An OGI camera will however pinpoint the source of the leak in the most efficient and effective way. 4. Combine an optical gas imaging camera with a sniffer probe. Use an OGI camera to visualize the leak and trace its source. Then, use a sniffer probe - a Toxic Vapor Analyzer (TVA) or Organic Vapor Analyzer (OVA) to quantify the leak. Combining an OGI camera with a sniffer probe is referred to as Smart LDAR. 5. Use all the features and functions on your OGI camera. Certain OGI cameras - including all of FLIR's GF-Series cameras - are dual-use systems. They can also be used for industrial maintenance inspections, including high- and low-voltage electrical installations, mechanical installations, pipework and insulation, ovens and many more. The thermographic function on your OGI camera will also help you determine the background temperature/energy the gas is absorbing. Unlike with other thermographic applications, your object of detection (gas) has no visual representation and it is moving constantly. Therefore, a continuous focus is most important and so is the thermographic capability to determine the temperature range settings. An OGI camera also allows you to record a movie to capture the movement and pinpoint the leak. It is always advised to take a visual image.
6. Keep it safe. A gas imaging camera is a quick, non-contact measuring instrument that can also be used in hard to access locations. It can detect small leaks from several meters away and big leaks from hundreds of meters away. It can even show leaks on moving transport vehicles, hereby greatly improving the safety of both the inspector and the plant. Thanks to their great performance, sensitivity and, with some cameras, also the High Sensitivity Mode (HSM), you can scan for leaks from a safe zone or even from a greater distance, compared to traditional gas detection methods. 7. Consider future industrial emissions regulations. Fugitive gas emissions contribute to global warming and pose deadly risks to both workers and people living close to these facilities. FLIR Optical Gas Imaging cameras detect dozens of volatile organic compounds, including the greenhouse gas Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF6), hereby efficiently contributing to a better environment. Optical gas imaging cameras also allow you to comply with new industrial emissions regulations & procedures as set by the new EU Industrial Emissions Directive (IED) and by some EPA regulations in the United Sates.
8. Keep track of your return on investment In many cases, the cost of the camera is paid for within its very first survey and in some cases with the finding of the very first leak. 9. Work with permits. OGI cameras in general are not Zone 1 ATEX certified. Therefore you will need to apply for a 'Hot Work Permit' or use it under a 'Permit to work scheme'. Remember, you can see significant and dangerous leaks with the right camera from a safe zone, even outside of the facility perimeter. 10. Follow training. Learn from experienced and qualified OGI users to get the most out of your camera. You might follow a training course by quality organizations such as the Infrared Training Center (http://www.infraredtraining.com). |
 |
 |